The consensus pathway for the management of uncontrolled asthma is available to view and download: full version or overview.
Up to 200,000 people in the UK have severe and uncontrolled asthma which has a significant impact on their quality of life.
Many are frequently admitted to hospital as an emergency and run the risk of serious side-effects from extended periods on high dose steroid-based medication. Current service provision is patchy, characterised by lengthy waits and wide variations.
Emerging biologic therapies offer better outcomes for large numbers of these people – but very few are receiving them.
Improving outcomes for patients with respiratory disease is one of the clinical priorities in the NHS Long Term Plan. The NHS Accelerated Access Collaborative (AAC) Rapid Uptake Products (RUP) programme includes improving access to asthma biologics by supporting improvements in pathways and practices to ensure more patients receive timely specialist care.
This programme has produced a consensus pathway which provides a set of standards for the care of adults with uncontrolled and severe asthma based on best practice. It is intended to be a blueprint, guiding clinicians, managers and commissioners on what optimal care should look like across the entire patient journey and leading to real improvements in outcomes.
The consensus pathway was launched at NHS ConfedExpo on 16 June 2022 where Oxford/Wessex Academic Health Science Networks delivered a session at the AHSN Network Innovation Zone on ‘Transforming asthma care through system-wide collaboration and innovation’.
The AAC asthma biologics programme is led by the Oxford AHSN on behalf of the AHSN Network.
Learn more about how the pathway was developed
The consensus pathway for managing uncontrolled asthma in adults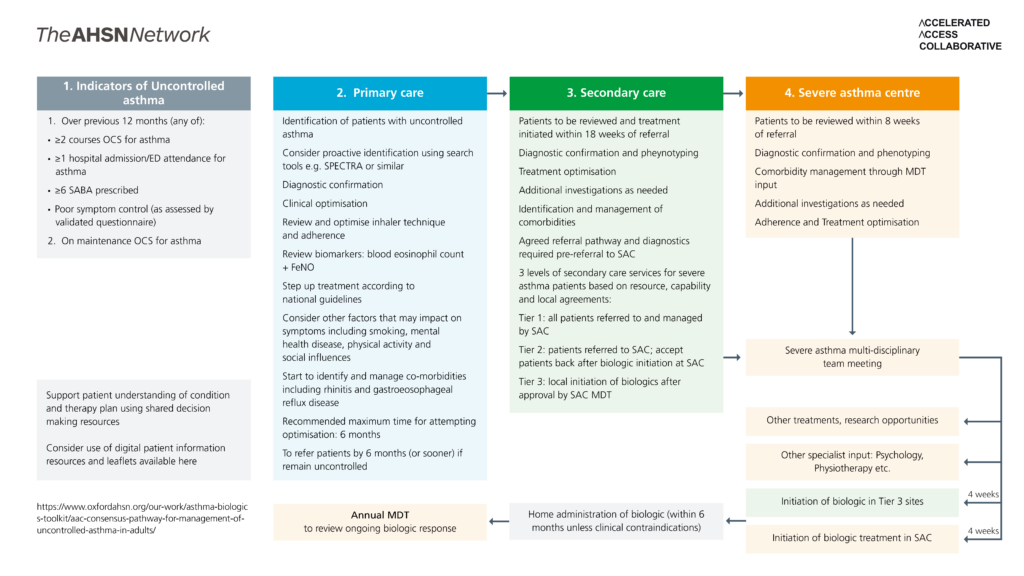
Each part of the pathway diagram above is detailed in the drop down boxes below.
- Over previous 12 months (any of):
- 2 courses OCS for asthma
- 1 hospital admission/ED attendance for asthma
- 6 SABA prescribed
- Poor symptom control (as assessed by validated questionnaire)
- On maintenance OCS for asthma
Support patient understanding of condition and therapy plan using shared decision making resources
Consider use of digital patient information resources and leaflets available here
Home administration of biologic (within 6 months unless clinical contraindications)
Identification of patients with uncontrolled asthma
Consider proactive identification using search tools e.g. SPECTRA or similar
Diagnostic confirmation
Clinical optimisation
Review and optimise inhaler technique and adherence
Review biomarkers: blood eosinophil count + FeNO
Step up treatment according to national guidelines
Consider other factors that may impact on symptoms including smoking, mental health disease, physical activity and social influences
Start to identify and manage co-morbidities including rhinitis and gastroeosophageal reflux disease
Recommended maximum time for attempting optimisation: 6 months
To refer patients by 6 months (or sooner) if remain uncontrolled
Patients to be reviewed and treatment initiated within 18 weeks of referral
Diagnostic confirmation and pheynotyping
Treatment optimisation
Additional investigations as needed
Identification and management of comorbidities
Agreed referral pathway and diagnostics required pre-referral to SAC
3 levels of secondary care services for severe asthma patients based on resource, capability and local agreements:
Tier 1: all patients referred to and managed by SAC
Tier 2: patients referred to SAC; accept patients back after biologic initiation at SAC
Tier 3: local initiation of biologics after approval by SAC MDT
Initiation of biologic in Tier 3 sites at 4 weeks
Patients to be reviewed within 8 weeks of referral
Diagnostic confirmation and phenotyping
Comorbidity management through MDT input
Additional investigations as needed
Adherence and Treatment optimisation
Severe asthma multi-disciplinary team meeting
Other treatments, research opportunities
Other specialist input: Psychology, Physiotherapy etc.
Initiation of biologic treatment in SAC at 4 weeks
Annual MDT
to review ongoing biologic response
Implementation resources
Understanding Opportunities for Improvements
Implementation Tools and Resources
Asthma Biologic Pathway Transformation Fund Projects
The Pathway Transformation Fund (PTF) has been made available to NHS providers to deploy innovative ideas to overcome barriers to the adoption of Asthma Biologics within their locality. A list of the PTF project sites is available here.



